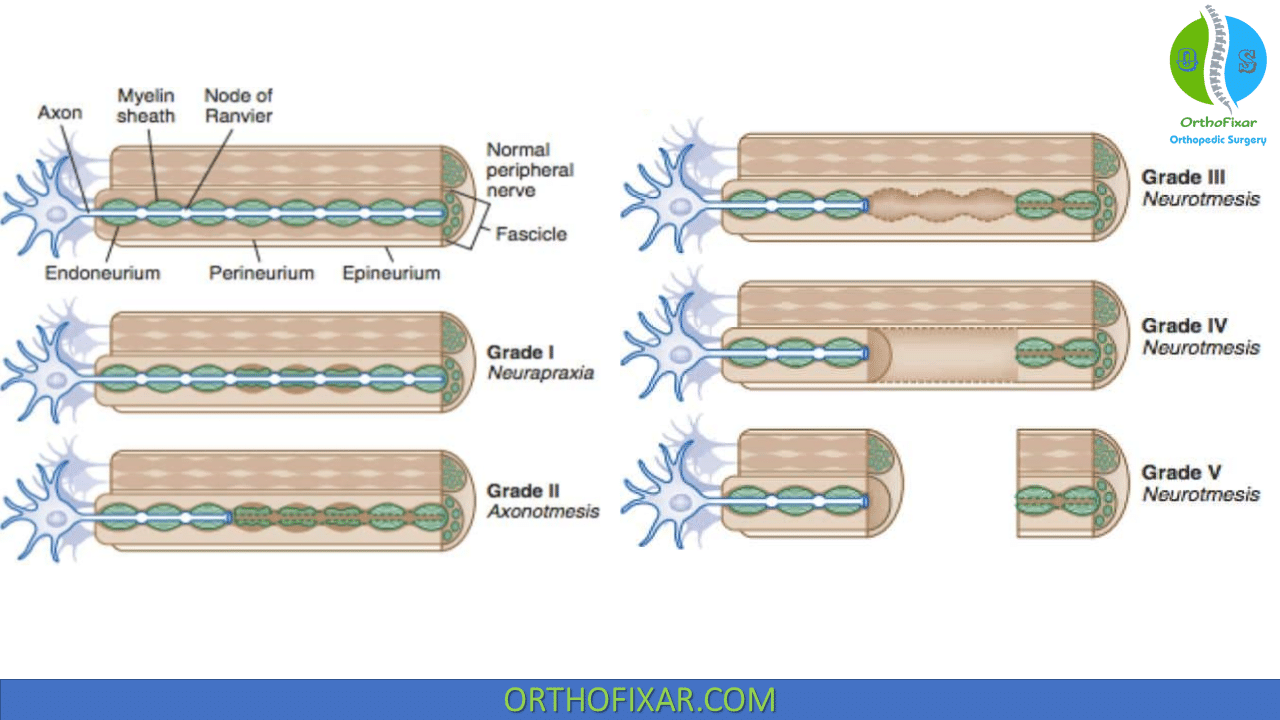
Classification Of Nerve Injuries OrthoFixar 2024
Neurotmesis: rotura anatómica del axon y tejidos conectores. Lesiones del nervio se puede clasificar en tres tipos: Neuropraxia - bloque fisiológico de la conducción del nervio con un axon sin una interrupción anatómica. Muchos niños con lesión del plexo braquial tienen neuropraxia y se recuperan espontáneamente porque neuropraxia.

NEUROLOGÍA Lesiones de los nervios periféricos según la clasificación de Seddon (1943)
En la actualidad, la clasificación más utilizada en las lesiones nerviosas periféricas es la Sunderland (7), que distingue cinco grados de lesión nerviosa. Esta clasificación tiene una correspondencia con el pronóstico de la lesión, por lo que, a mayor grado, peor pronóstico de recuperación funcional.

Parálisis del sábado noche
In 1951, Sunder- land [20] expanded Seddon's classification to five degrees of peripheral nerve injury (Fig. 1). The 1 st degree is essentially the same as neuropraxia of Seddon classification.
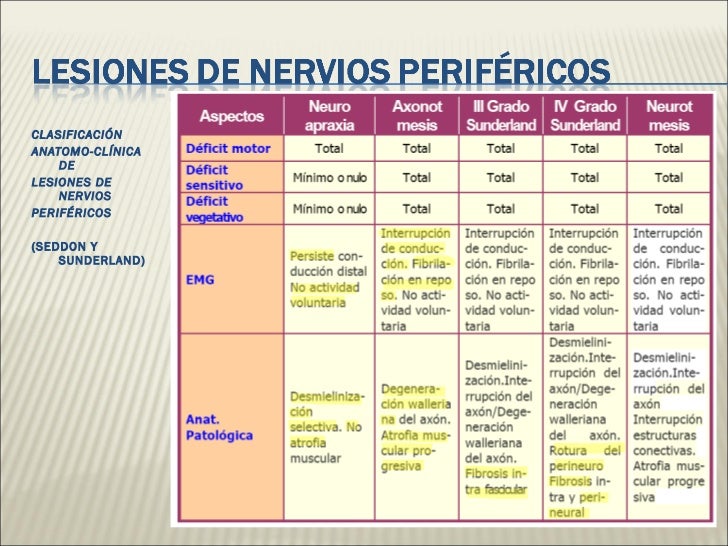
Lesion de nervio periferico
In 1953, Sunderland expanded Seddon's classification from three to five degrees of peripheral nerve injury. The injuries are arranged in ascending order of severity from the first to the fifth degree and affect successively (1) conduction in the axon, (2) the continuity of the axon. (3) the endoneurial tube and its contents, (4) the fascicle.

Sunderland Classification Of Nerve Injury Nerve Injuries Diagnosis Evaluation And Management 1
By Chris Faubel, MD — Understanding nerve injury classification is essential for prognostic value clinically.. Some basic anatomy, along with the two classification systems, and their corresponding EMG findings need to be learned and remembered.. Two classification systems exist (and are frequently tested in various exams):. Seddon's classification (neuropraxia, axonotmesis, neurotmesis)

Overview of Seddon and Sunderland classifications. Download Scientific Diagram
Sea cual sea su localización, las lesiones traumáticas de los nervios se clasifican en función de la gravedad. La clasificación de Seddon en tres órdenes de gravedad creciente ha sido completada por la de Sunderland en cinco grados (Cuadro 1). En la práctica, las que se observan con más frecuencia son las lesiones de grado 5 con pérdida.

PPT Peripheral nerve injuries PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID521215
Sir Herbert Seddon (1903-1977), the Sunderland classifica-tion scheme is more complex [3]. Sir Sydney Sunderland. Herbert John Seddon (1978) Lancet 1 (8054):54 5. Kaya Y, Sarikcioglu L (2014) Sciatic nerve injury models. Turkiye Klinikleri J Neurol-Special Topics (in press) 6. Maggi SP, Lowe JB 3rd, Mackinnon SE (2003) Pathophysiology of

ELECTROESTIMULACIÓN MUSCULAR Mind Map
The Seddon and Sunderland classifications have been used by physicians for peripheral nerve injury grading and treatment. While Seddon classification is simpler to follow and more relevant to electrophysiologists, the Sunderland grading is more often used by surgeons to decide when and how to intervene. With increasing availability of high.

Classification of Peripheral Nerve Injury Seddon's classification , Sunderland's
Seddon, en 1943, introdujo una clasificación funcional que describía tres tipos de lesiones nerviosas: la neurapraxia, la axonotmesis y la neurotmesis. Sunderland desarrolló la clasificación de Seddon al incluir el primer grado lesional (neurapraxia), el segundo grado (axonotmesis) y la neurotmesis como quinto grado (Fig. 1).

Seddon and Sunderland nerve injury classification and incidence during... Download Scientific
Clasificación: Las lesiones de los nervios se dividen en neuropraxia, axonotnesis y neurotmesis (tabla 1). Tabla 1. Clasificación de las lesiones de nervio según Seddon y Sunderland. Grados de Seddon Tipos de Sunderland Descripción Neuropraxia I Pérdida de la conducción Axonotmesis II Pérdida de la continuidad axonal.
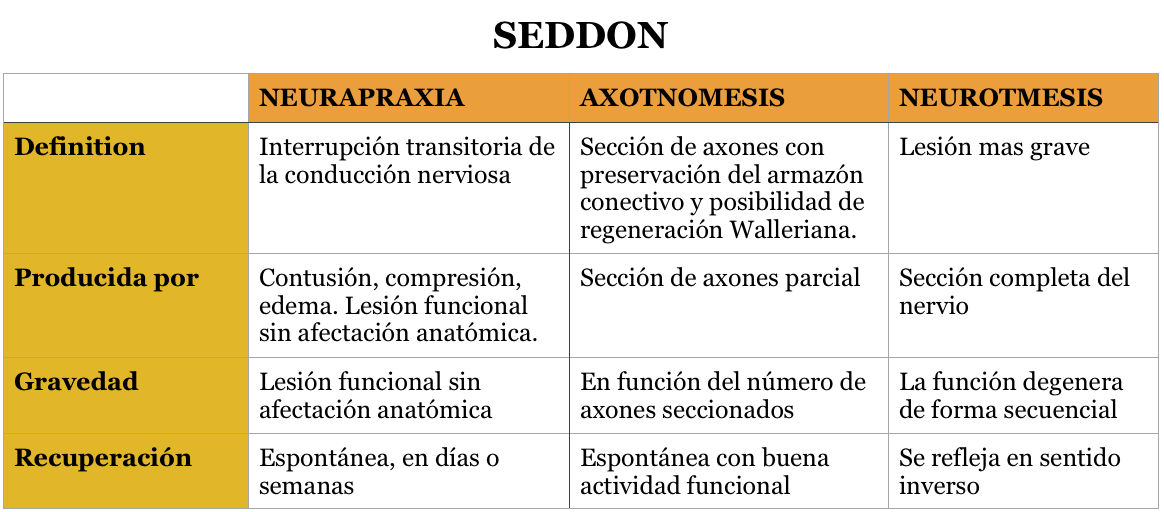
ELECTROESTIMULACIÓN MUSCULAR Mapa Mental
Clasificación de Seddon. Considerando la gravedad, estos tipos de la clasificación de Seddon son: . Neuropraxia. También llamada axonopraxia.Es la condición en la cual, como resultado de un accidente politraumatico, contusión, compresión o isquemia, se produce falla o pérdida de la conducción nerviosa debida a un corte, sin poderse demostrar daño estructural del nervio.

Neuropatías por atrapamiento generalidades y tratamiento rehabilitador
Nerve injury classification assists in prognosis and determination of treatment strategy for nerve injuries.Classification was described by Seddon in 1943 and by Sunderland in 1951. In the lowest degree of nerve the nerve remains intact, but signaling ability is damaged, termed neurapraxia.In the second degree the axon is damaged, but the surrounding connecting tissue remains intact.

Clasificacion de Nervios Perifericos Seddon & Sutherland [PDF Document]
Seddon HJ (1971) Surgical disorders of the peripheral nerves. Churchill Livingstone, Edinburgh. Google Scholar Sir Herbert Seddon, 1903-1977 (1978). J Bone Joint Surg Br 60-B (2):276-278. Sunderland S (1951) A classification of peripheral nerve injuries producing loss of function. Brain 74(4):491-516
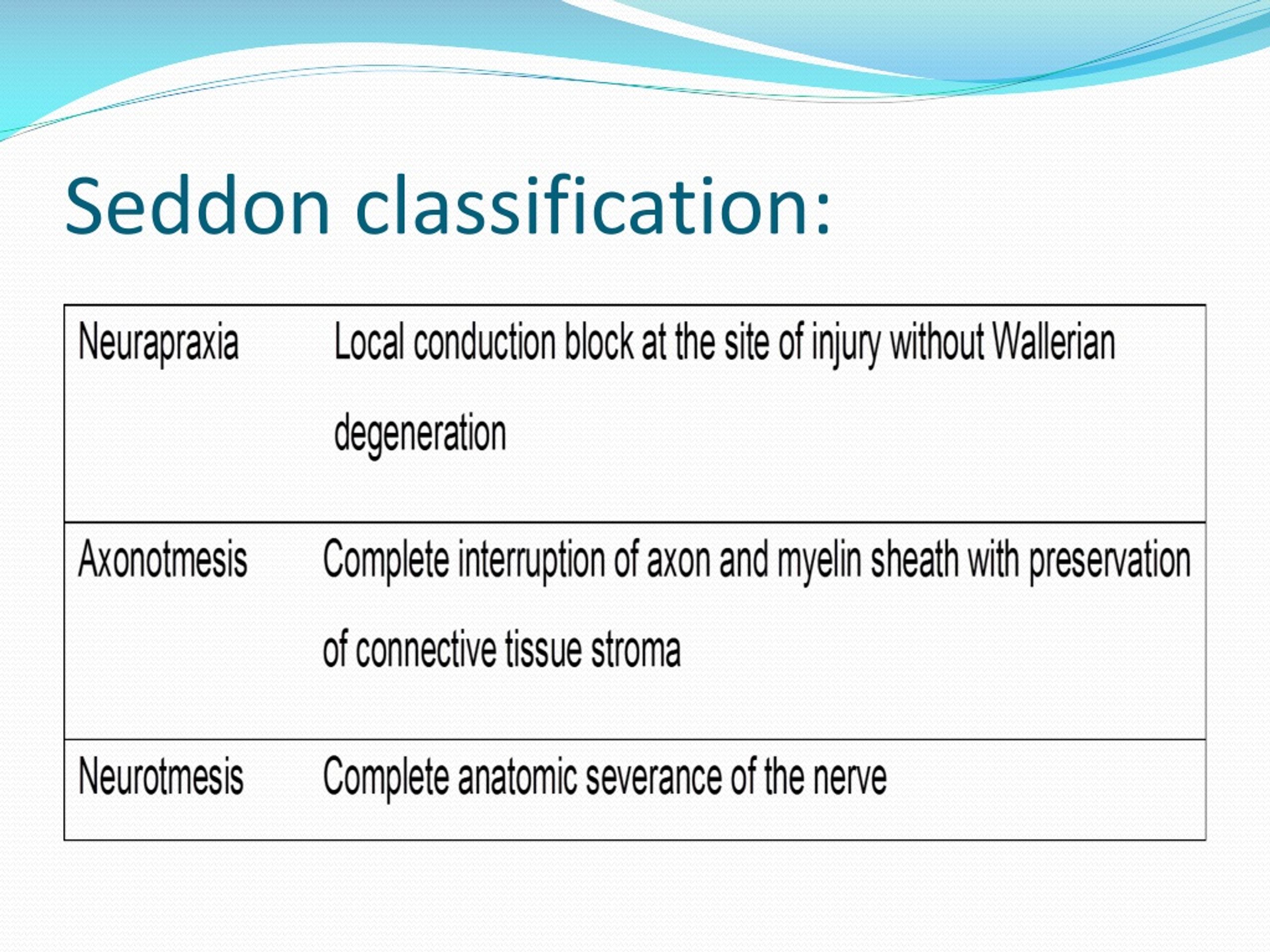
PPT NERVE INJURIES PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID226964
Seddon (1943) [13] was the first to implement a classification for nerve injuries. They were classified into three categories based on presence of demyelination and damage extension to the axons.
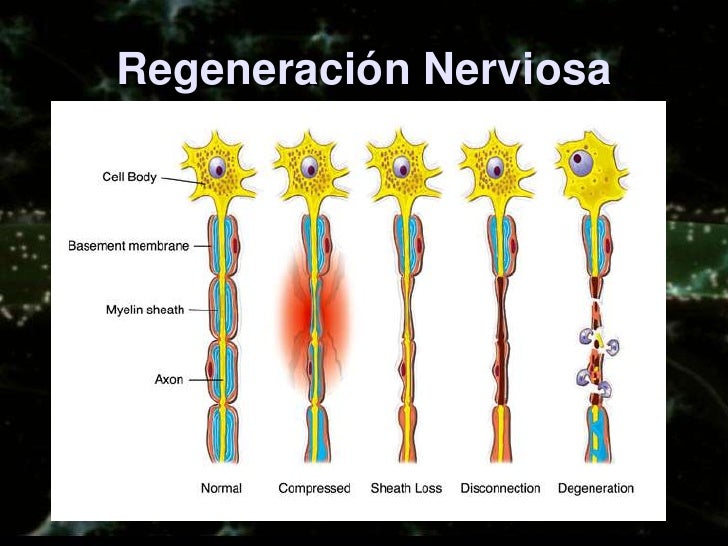
qqqq
o Seddon: 3 categorías de lesión: neurapraxia, axonotmesis y neurotmesis o Sunderland: 5 grados (axonotmesis subdividida en 3 según endo, peri o epineuro intacto) Neurapraxia: daño localizado en la mielina (a menudo por compresión) con axón indemne sin degeneración distal Axonotmesis: disrupción de axón y mielina, con epineuro indemne.

Sunderland Classification Classification of Peripheral Nerve Injury Seddon's
Fig. 2.1 Seddon and Sunderland classification of nerve injury based upon histological neural changes 2.3.1.1 Neurapraxia Neurapraxia is seen as motor paralysis, and it is the mildest injury type that is transient. There is no effect on nerve continuity. The transient nature of this injury is believed to be caused by a temporary disturbance in….
- Calorías De Muslo De Pollo
- National Lampoon S Van Wilder Reparto
- Cuanto Tiempo Es De Chetumal A Holbox
- Jack Kent Cooke Net Worth
- Pearson Programa De Televisión Reparto
- Que Ingredientes Lleva La Lasaña
- Catálogo De Donantes De Esperma En Argentina
- Bailes De La Zona Sur
- Olga María Del Carmen Sánchez Cordero Dávila
- Características Del Ciclo Del Nitrógeno